“Early Detection Saves Lives: Comprehensive Oral Cancer Screening”
Oral Cancer Screening Introduction:
Oral cancer screening is a crucial procedure designed to detect early signs of cancer in the mouth, lips, and throat. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes and increase survival rates. This guide provides comprehensive information about oral cancer screening, its importance, procedures, and what to expect during an examination.
Importance of Oral Cancer Screening
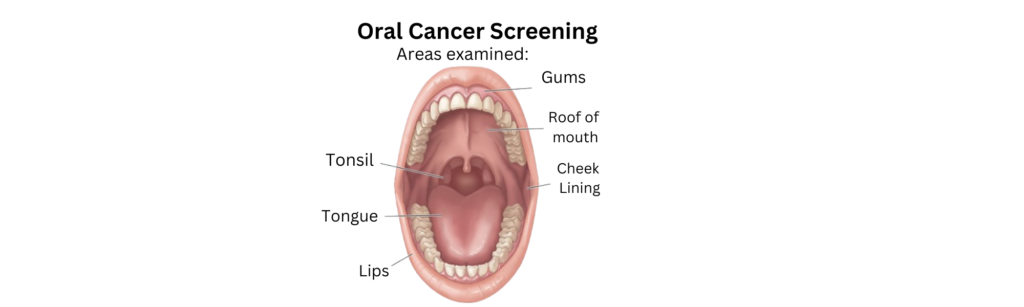
Oral cancer can develop in any part of the mouth, including the lips, gums, tongue, roof and floor of the mouth, and the inner lining of the cheeks. Regular screenings can help identify precancerous conditions or early-stage cancer before symptoms become severe.
Key Benefits:
- Early Detection: Identifies abnormal cells before they develop into cancer.
- Better Prognosis: Early treatment is more effective, improving survival rates.
- Prevention: Helps in removing precancerous lesions before they turn malignant.
- Peace of Mind: Regular screenings provide reassurance and maintain oral health.
Who Should Get Screened?
Everyone is at risk of developing oral cancer, but certain factors increase the likelihood:
- Age: Individuals over 40 years old.
- Tobacco Use: Includes smoking and smokeless tobacco.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking.
- HPV Infection: Human papillomavirus infection.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight, especially affecting the lips.
- Family History: Genetic predisposition to cancer.
Screening Procedures
Oral cancer screening is typically quick, non-invasive, and painless. Here’s what to expect:
Visual Examination:
- External Check: The dentist or oral health professional will examine your face, neck, lips, and mouth for any signs of swelling, lumps, or irregularities.
- Internal Check: The inside of your mouth, including the gums, lining, tongue, and roof and floor of the mouth, will be inspected for sores, discolored tissues, or other abnormalities.
Physical Examination:
- Palpation: The dentist will feel for any lumps or irregularities inside your mouth and around your jaw and neck area.
Additional Diagnostic Tools:
- Toluidine Blue Stain: A special dye may be applied to highlight abnormal cells.
- Fluorescence Staining: Special lights help to differentiate between healthy and abnormal tissue.
- Brush Biopsy: A small brush is used to collect cells from suspicious areas for laboratory analysis.
- Scalpel Biopsy: If needed, a small tissue sample is surgically removed for further examination.
What to Expect
During your oral cancer screening, you can expect a thorough examination of your oral cavity and adjacent areas. The process is usually quick, lasting only a few minutes unless further investigation is needed. If abnormalities are detected, additional tests or referrals to specialists may be recommended.
Follow-Up and Next Steps
If any suspicious areas are found during the screening, your dentist may suggest:
- Further Testing: Additional diagnostic procedures to confirm findings.
- Specialist Referral: Consultation with an oncologist or oral surgeon for further evaluation.
- Regular Monitoring: More frequent check-ups to monitor any changes in the condition.
Preventive Measures
While screening is essential, preventive measures can also reduce the risk of oral cancer:
- Avoid Tobacco: Do not smoke or use smokeless tobacco products.
- Limit Alcohol: Consume alcohol in moderation.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Sun Protection: Use lip balm with SPF and avoid excessive sun exposure.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Routine visits to your dentist for examinations and cleanings.
Conclusion
Oral cancer screening is a vital part of maintaining your oral health and overall well-being. Early detection can save lives, making regular screenings an important practice. If you have any risk factors or concerns, schedule an appointment with your dentist today.

